Microplastics may form when larger pieces of plastic break into pieces after exposure to elements for a long time. Around 36 percent of the 400 million tons of plastic waste that we generate every year is used in packaging. When plastic was first invented in the early 1900s, it was thought to be a highly robust material. Before recent research that revealed it was actually causing harm to the environment, it was considered to be a revolutionary material.
Plastic is not biodegradable, so it is not able to break down quickly, but over a longer time, it breaks down into small pieces that are known as microplastics. Microplastics secondary to plastic may end up in soil or in water, and could then be taken up by plants. Microplastics are tiny particles of plastic that are less than 5 millimeters in size. Because of their size, microplastics can be easily consumed in water, food items, and the surrounding environment.
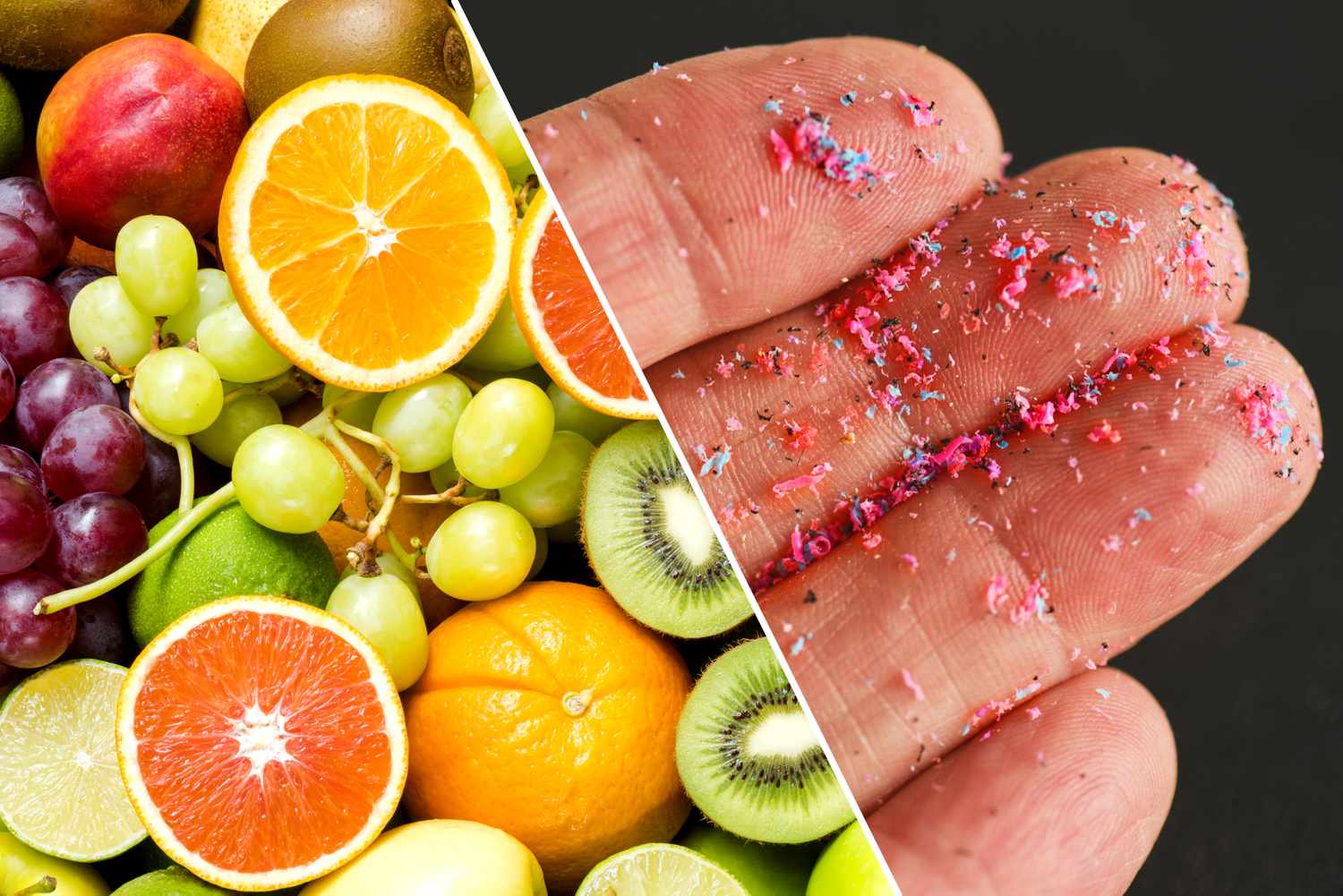
Numerous studies have identified microplastics in both vegetables and fruits. Packaging made of plastic that is used to store and transport fruits and vegetables could also be a source of microplastics. Plants are able to absorb microplastics via their root systems. These will then be absorbed by the edible components that the plant. Microplastics are able to be introduced into the food chain via the soil.
Fruits and Vegetables Contaminated with Microplastics
Based on a study done by University of Catania scientist Margherita Ferrante, the fruit contained an increased amount of microplastics than vegetables. This could be because fruit trees are a bit older and are subjected to greater environmental pollution. A different study showed that microplastics smaller than 10 mm varied between 52,050 and 233,000 particles/g according to the samples of vegetables. The most significant microplastics identified in the study came from lettuce. Microplastics were also found in other foods, including wine, beer, and table salt. They also found rice and honey. Here are some foods and vegetables most likely to be contaminated with microplastics:
- Fruits like apples: These are among the most polluted fruits and have, on average, 195,500 particles of plastic per Gram.
- Carrots: Carrots are among the most susceptible vegetables, averaging over 100,000 pieces of plastic per gram.
- Lettuce: It has been discovered to contain an average of over 100,000 pieces of plastic for every gram.
- Broccoli: Broccoli is one of the most polluted vegetables, with over 100,000 pieces of plastic in a gram.
How Do Fruits and Vegetables Contain Microplastics?
Microplastics may end up in vegetables and fruits in a variety of ways. Here are a few ways microplastics may be found in fruits and vegetables:
Plants absorb microplastics through their root systems. These will then be accumulated within the edible parts that the plant produces. This means that microplastics could be introduced into the food chain via the soil.
Microplastics may form when larger pieces of plastic break into pieces after exposure to elements for a prolonged amount of time. The secondary microplastics may be found in soil and in the water, which will then be absorbed by plants.
Microplastics are found in irrigation water, which could then be absorbed by plants.
Plastic packaging used for the storage and transportation of vegetables and fruits can contain microplastics.
According to a study conducted by University of Catania scientist Margherita Ferrante, the fruits had the highest amount of microplastics than vegetables. This is because they are older and are exposed to greater environmental pollutants. Another study revealed that apples are among the most polluted fruits and that carrots have the highest level of contamination. Affected vegetables. The amount of microplastics found in both vegetables and fruits could vary based on the kind of food item and the location in which it was cultivated.
In conclusion, microplastics could end up in fruit and vegetables in many ways, such as absorption through roots, secondary microplastics in irrigation water, as well as plastic packaging. It is essential to take steps to minimize exposure to microplastics found in food products, including eating fresh, whole foods instead of processed food items, washing vegetables and fruits thoroughly before eating them, and avoiding plastic containers or utensils while cooking or storing food items, assisting efforts to decrease the impact of plastics on the environment, and encouraging sustainable methods of living.
Risks to Health from Microplastics
Microplastics have been recognized as toxicological vectors. That means they may adsorb other chemicals onto their surfaces before getting into contact with human cells, which can enhance their toxic effects. However, the long-term health risks of consuming microplastics are not yet comprehended. It is necessary to conduct more research to assess the possible dangers of microplastics found in food items.
The following list includes some of the health hazards linked to consuming microplastics.
- Microplastic exposure is believed to pose a human reproductive risk.
- Microplastics may limit the diversity of the gut microbiome. This could result in negative health consequences.
- A hormonal imbalance in the digestive system could be the result of being exposed to plastics.
- Microplastics can absorb toxic substances, making it more likely to develop an infection within the digestive tract.
- Inhaling microplastics can create oxidative stress within the lung and airways, resulting in respiratory issues.
- Microplastics have been proven to Fruits and Vegetables Containing Microplastics and carcinogenic impacts.
- Microplastics, which could cause digestive issues and infections since they absorb dangerous substances, were discovered in small studies to be found inside the human stomach as well as the bloodstream.
- Exposure to microplastics has been reported to pose a risk of digestion for people, including cancer.
It is crucial to remember it is important to note that the health risks of eating microplastics aren’t yet understood fully, and more research is required to understand the risks associated with microplastics present in food products. However, in light of the health risks that come with eating microplastics, it’s important to take measures to minimize exposure to microplastics, for example, eating fresh, whole foods instead of processed ones washing vegetables and fruits thoroughly before eating them, not using plastic containers and utensils for cooking or storing food and assisting efforts to decrease the impact of plastics on the environment and encourage sustainable practices.





